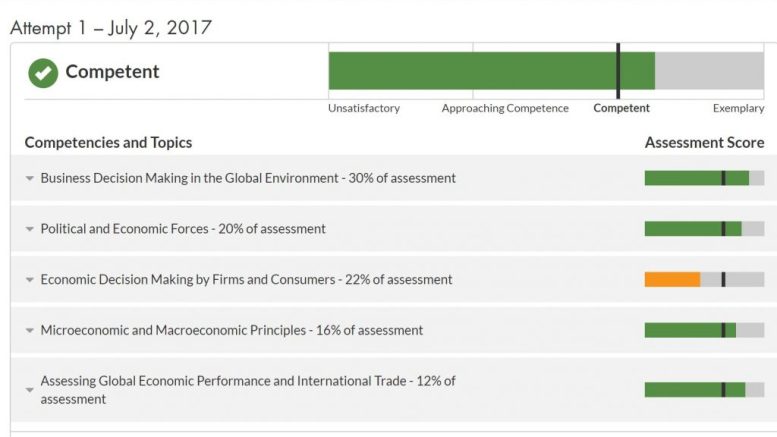
Well, look at that. I am a competent manager when it comes to Global Economics. I’ll be honest it was more difficult than I was expecting. But I passed and now it is on to the accounting course. Now that should be some exciting reading.
The Global Economics for Managers course is part of WGU’s competency-based MBA program. It focuses on applying macroeconomic and microeconomic principles in a global business environment. It explores international trade theory, market structure, and globalization. This prepares managers to making informed global business decisions.
Condensed Exam Study Guide (Fast Review)
Competency 1 — Business Decision‑Making in the Global Environment
Key Ideas
Comparative Advantage: Produce what you’re relatively best at; trade for the rest.
Specialization & Gains from Trade: Countries/firms benefit by specializing.
- Globalization Views (Long‑run, Pendulum, New Force): Integration shifts over time.
- Institution‑Based View vs. Resource‑Based View: Success depends on rules (laws, culture) and unique internal capabilities.
Competency 2 — Political & Economic Forces
Key Ideas
- Political systems: democracy, theocratic, totalitarian. (Common exam topic from student reports.)
- Economic systems: market, command, mixed economies.
- Policy tools: tariffs, trade barriers, government intervention.
Competency 3 — Economic Decision‑Making by Firms & Consumers
Key Ideas
- Indifference Curves & Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS): Consumer choice theory.
- Cost Curves: Marginal cost, fixed vs. variable costs. If MR > MC → Increase production.
- Market Structures: Perfect competition vs. monopoly vs. oligopoly. Barriers to entry.
Competency 4 — Microeconomic & Macroeconomic Principles
Microeconomics
- Supply & Demand Shifts: How equilibrium price/quantity changes with shocks. (Common OA pattern.)
- Elasticity: Responsiveness to price changes.
Macroeconomics
- Exchange Rates: Interest rate changes influence currency flows.
- Federal Reserve Tools: Open market operations, reserve ratio, discount rate.
- Inflation & Monetary Policy: Buying bonds increases money supply; selling bonds decreases it. (Frequently cited in OA discussions.)
Competency 5 — Global Economic Performance & International Trade
Key Ideas
- FDI (Foreign Direct Investment): Horizontal vs. vertical.
- International Institutions: IMF, WTO roles (general knowledge).
- Exchange Rate Dynamics: Currency appreciation/depreciation impact trade.
- Porter’s Diamond & Global Strategies (Dodger, Defender, Extender, Contender).

Be the first to comment on "Passed Global Economics"