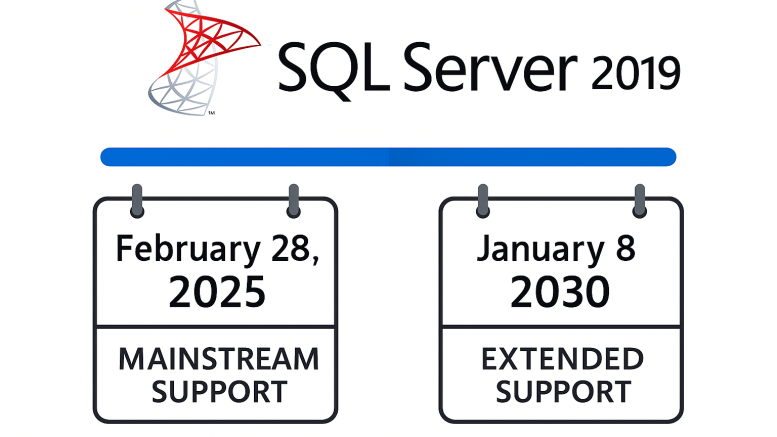
Mainstream support for Microsoft SQL Server 2019 will end on February 28, 2025. After this date, Microsoft will no longer provide new features, functionalities, or general fixes for this version. However, extended support for SQL Server 2019 will continue until January 8, 2030. More information here. Here are the most recent Security Updates for SQL Server 2019 from the SQL Server Blog announcements.
February 2025
- Security Update of SQL Server 2019 CU32 (February 28, 2025) KB5054833 – Cumulative Update 32 for SQL Server 2019
- 3907024: Fixes an issue in which patching a read-scale availability group causes the availability group on the patched replica to be removed.
- Security Update of SQL Server 2019 CU31 (February 24, 2025) KB5049296 – Cumulative Update 31 for SQL Server 2019
- 3666818: Fixes an issue with the business rule item for the domain-based attribute (DBA) option. This is for when you use Master Data Services.
- 3548672: Fixes various assertion failures.
- 3794235: Fixes a race condition that you encounter during flush operations when configuring control.alternatewritethrough = 1. Which causes extended waits for some transactions.
- 3791616: Fixes an issue in Database Mail. Specifically, which information is logged into the sysmail_log system table and sysmail_event_log view in the msdb database might be stored and displayed as “???”
- 3677986: FIX: Scalar UDF Inlining issues in SQL Server 2022 and 2019 (KB4538581)
- 2431765: Adds the following error 18749 when you use the MaxCmdsInTran parameter for the Log Reader Agent and change data capture (CDC) is enabled on the database:
- 3739570: Fixes an issue in which the second article might not have updates correctly replicated if accelerated database recovery (ADR) is enabled on the database using replication with two articles for a single table.
- 3801166: Fixes an issue in which the manual change tracking cleanup stored procedure incorrectly sets the invalid cleanup version to negative when the TableName parameter isn’t passed.
- 3221735: Fixes an issue in which updating permissions on the newly added column fails if you previously denied permissions on an existing column.
- 3800645: Data Quality Services (DQS) is only supported in SQL Server Enterprise and Developer editions. Before the fix, the operation is completed successfully when you try to install DQS in the Standard or Web edition.
SQL Server Delivery Model:
The SQL Server team uses a scheduled delivery model for releasing fixes and product updates. These security updates are part of Microsoft’s Servicing models for SQL Server that started with the release of SQL Server 2017. In the scheduled delivery model, a customer can receive a fix to address their most critical situations in a reasonable time. Therefore, the SQL Server team has created the following delivery mechanisms.
- A General Distribution Release (GDR) update is a patch that Microsoft releases for critical issues. They often address security problems, but not exclusively. They may be available through Windows Update and sometimes are for versions no longer supported.
- A Cumulative Update (CU) release includes all the security fixes, improvements. Occasionally, also included are new features for a major version of SQL Server since its Release to Manufacture (RTM). These are available every month for the first year of a version. Then approximately every two months until mainstream support stops. (Typically, 4-5 years). As of January 2024, SQL Server 2022 is on a bi-monthly servicing release schedule. SQL Server 2019 has been transitioned to extended support as of Feb 28, 2025.
Choosing between GDR or CU
You can choose either GDR or CU updates depending on your corporate policy or patching plan. But you cannot easily switch from CU to GDR. It is recommended to stay up to date on the latest CU path. Test the updates in a development or staging environment before deploying to production.
So why choose the GDR path? One main reason is that testing non-critical fixes can be costly and time-consuming. An organization may lack the resources to verify all the possible changes. So only critical GDR updates are implemented in those environments.
To see which current GDR or CU update is available, first determine which version and edition of SQL Server Database Engine is running. Next, download the SQL Server builds Excel workbook from https://aka.ms/sqlserverbuilds that contains a summary list of builds and their current support lifecycle. The Excel file also contains detailed fix lists for SQL Server 2022, SQL Server 2019, and SQL Server 2017.




Be the first to comment on "Mainstream support for Microsoft SQL Server 2019"