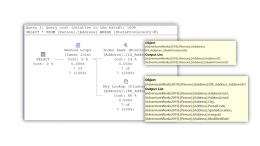
Execution Plans – Table Operators
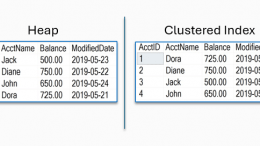
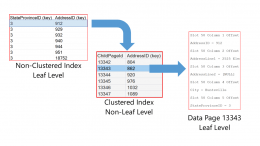
How to read Heap and Clustered Index table operators in a SQL Server Execution Plan. One way of determining if a table is structured as a Heap or a Clustered Index is to look at the table operators from the Execution Plan.